Maize Fodder: Unlock Agricultural Success
Maize Fodder is an important food for animals on farms. It gives them energy, fiber, and nutrients to grow and stay healthy. Farmers use it to feed cows, pigs, chickens, and other animals. But giving each animal the right amount of corn fodder is important. In this article, we’ll talk about why giving animals the right amount of balancing corn silage rations is important and how to ensure they have a balanced diet.
Table of Contents
Understanding Corn fodder
What is Maize Fodder?
Maize silage is a forage made from the whole corn plant, including the grain and the stalk. It is harvested at a specific moisture content and ensiled to preserve its nutritional value. The fermentation process converts sugars in the plant material into organic acids, creating a stable feed source.
Nutritional Value of Corn Fodder
Corn fodder is an excellent source of energy and fiber. It contains carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, and vitamins necessary for animal growth and maintenance. The nutritional composition of maize silage can vary depending on factors such as corn variety, maturity stage, and ensiling conditions.
Balancing Maize Fodder Rations
Importance of Balancing Rations
Balancing rations involves formulating diets that meet the nutritional needs of livestock while optimizing production performance. By considering the specific requirements of each animal species, we can ensure a balanced intake of energy, protein, fiber, minerals, and vitamins, leading to improved growth, reproduction, and overall health.
Factors to Consider
When balancing maize fodder rations, several factors need to be considered. These include the animal’s age, weight, production stage, desired growth rate, and environmental conditions. It is essential to assess the nutrient content of maize silage and supplement it with other feed ingredients to achieve a well-rounded diet.
Maize Fodder Rations for Dairy Cows
Energy and Protein Requirements
Dairy cows have high energy and protein demands due to milk production. Balancing their rations involves providing sufficient energy from balancing maize fodder ratios while ensuring an adequate protein source such as soybean meal or other protein supplements. The energy-to-protein ratio is crucial for maintaining milk production and reproductive performance.
Mineral and Vitamin Supplementation
In addition to energy and protein, dairy cows require specific minerals and vitamins for optimal health and milk quality. Balancing maize silage rations involves supplementing with minerals like calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and vitamins such as A, D, and E to meet their nutritional needs.
Fiber Content and Digestibility
Fiber is vital in maintaining rumen health and promoting proper digestion in dairy cows. Corn fodder is an excellent dietary fibre source, but its digestibility can vary. Balancing rations requires considering the fiber content and ensuring a balance between digestible and indigestible fiber to support rumen function
Maize Fodder Rations for Beef Cattle
Growth and Maintenance Requirements
Beef cattle have different nutritional requirements based on their growth stage and purpose. Balancing corn fodder rations for beef cattle involves providing adequate energy for growth and maintenance. Depending on the desired endpoint, different energy-to-protein ratios can be adjusted to achieve the desired level of marbling and finish.
Feeding maize Silage to Calves
maize silage can be introduced to beef calves early to support their growth and development. However, care should be taken to ensure a gradual transition and avoid digestive upsets. Balancing rations for young beef calves involves providing a mix of milk replacer, starter feed, and small amounts of corn fodder.
Feedlot Diets
In the feedlot, maize silage serves as a staple component of finishing diets for beef cattle. Balancing rations requires considering energy density, protein supplementation, and the inclusion of other feed ingredients such as grains, protein concentrates, and roughage to optimize growth and meat quality
Maize Fodder Rations for Swine
Nutrient Requirements
Swine have specific nutrient requirements for growth, reproduction, and overall health. Balancing maize silage rations for swine involves meeting their energy needs by including corn fodder and supplementing with other grains and protein sources to achieve the desired growth rate and lean muscle development.
Feeding Strategies
maize silage can be used as part of a balanced ration for swine, but its inclusion should be carefully managed. The high fibre content of corn fodder can impact nutrient digestibility and feed efficiency in swine. Balancing rations for swine involves adjusting the level of maize silage and incorporating enzymes or other additives to enhance nutrient utilization.
Maize Fodder Rations for Poultry
Energy and Protein Needs
Poultry requires diets rich in energy and protein for growth, feathering, and egg production. Balancing corn fodder rations for poultry involves combining maize silage with other energy-dense ingredients such as grains, oilseeds, and protein supplements like soybean meal or fishmeal to provide a well-rounded diet.
Supplementing with Other Feed Ingredients
While maize silage can contribute to poultry diets’ energy and fiber content, it may not provide all the necessary nutrients. Balancing corn sillage rations for poultry includes supplementing with vitamins, minerals, and amino acids to meet their nutritional requirements and promote optimal growth and egg production.
Considerations for Balancing Rations
Feed Quality and Testing
To accurately balance rations, it is essential to regularly evaluate the quality of corn fodder and other feed ingredients. Testing for moisture content, nutrient composition, and potential contaminants allows for precise formulation and adjustments to meet the nutritional needs of livestock.
Adjusting Rations for Different Stages
Livestock nutritional requirements vary at different growth, reproduction, and lactation stages. Balancing rations involves adjusting the proportions of corn fodder and other feed ingredients to meet the changing demands of animals throughout their life cycle.
Optimizing Silage Rations: Key Considerations
Assess the nutritional requirements of the animals: Determine the specific needs of the livestock in terms of energy, protein, fibre, vitamins, and minerals. This information can be obtained through professional consultation or referring to nutritional guidelines for the particular species.
Analyze the quality of available silage: Conduct a laboratory analysis of the hay to assess its nutrient composition, including dry matter, crude protein, fiber levels, and energy content. This analysis helps determine the starting point for ration formulation.
Meeting Livestock Nutritional Needs: Best Practices
Assess nutritional requirements: Determine the specific needs of the livestock in terms of energy, protein, fibre, vitamins, and minerals. Consider factors such as age, weight, production stage, and breed to determine the nutritional requirements accurately.
Analyze available feed sources: Evaluate the nutrient composition and quality of available feed sources, including forages, grains, concentrates, and supplements. Consider factors such as digestibility, protein content, energy content, and potential nutrient deficiencies.
Effective Silage Feeding: Strategies for Success
Proper storage and preservation: Ensure the silage is properly harvested, stored, and preserved to maintain its nutritional quality. Respond to moisture content, compaction, and additives like inoculants to enhance fermentation and minimize spoilage.
Adequate feeding management: Implement a consistent feeding schedule and provide sufficient quantities of fodder to meet the animal’s nutritional requirements. When determining the feeding rate, consider the animal’s size, production stage, and environmental factors.
Balancing Maize Fodder for Dairy Cows: Best Practices
Formulate a balanced ration: Use the balancing corn fodder ration analysis and the cows’ nutritional requirements to formulate a balanced ration. As needed, add feed sources such as grains, forages, concentrates, and supplements to address any nutrient deficiencies or imbalances.
Monitor performance and adjust: Regularly evaluate the cows’ milk production, body condition, and overall health to ensure the ratio meets their needs. Adjust the ratio based on observed changes, aiming for optimal milk production, reproductive performance, and cow well-being.
Achieving Optimal Beef Cattle Rations with Maize Fodder
Assess beef cattle nutritional requirements: Determine the specific nutritional needs of the beef cattle in terms of energy, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Consider age, weight, production stage, and breed to accurately determine their requirements.
Analyze maize silage composition: Conduct a laboratory analysis to evaluate its nutrient composition, including dry matter, protein levels, fibre content, energy value, and mineral composition. This analysis helps determine the starting point for ration formulation.
Optimizing Swine Rations with Maize Fodder
Optimize inclusion levels: Determine the optimal inclusion levels of maize silage in the ration based on its nutrient composition and the nutritional requirements of the swine. Consider energy density, digestibility, and palatability to achieve an efficient and effective ratio.
Seek professional advice: Consult with a nutritionist or swine industry expert to ensure the ration optimization process considers the swine herd’s specific needs, industry standards, and best practices for swine nutrition. Their expertise can provide valuable insights and guidance for achieving optimal swine rations with maize silage.
Incorporating Corn fodder in Poultry Rations
Consider digestibility and palatability: Evaluate the digestibility and palatability of corn fodder in poultry diets, making adjustments to the inclusion level and processing methods if necessary.
Seek professional guidance: Consult a poultry nutritionist or industry expert to ensure the successful incorporation of corn fodder in poultry rations, taking into account industry guidelines and best practices
Corn fodder nutritional value
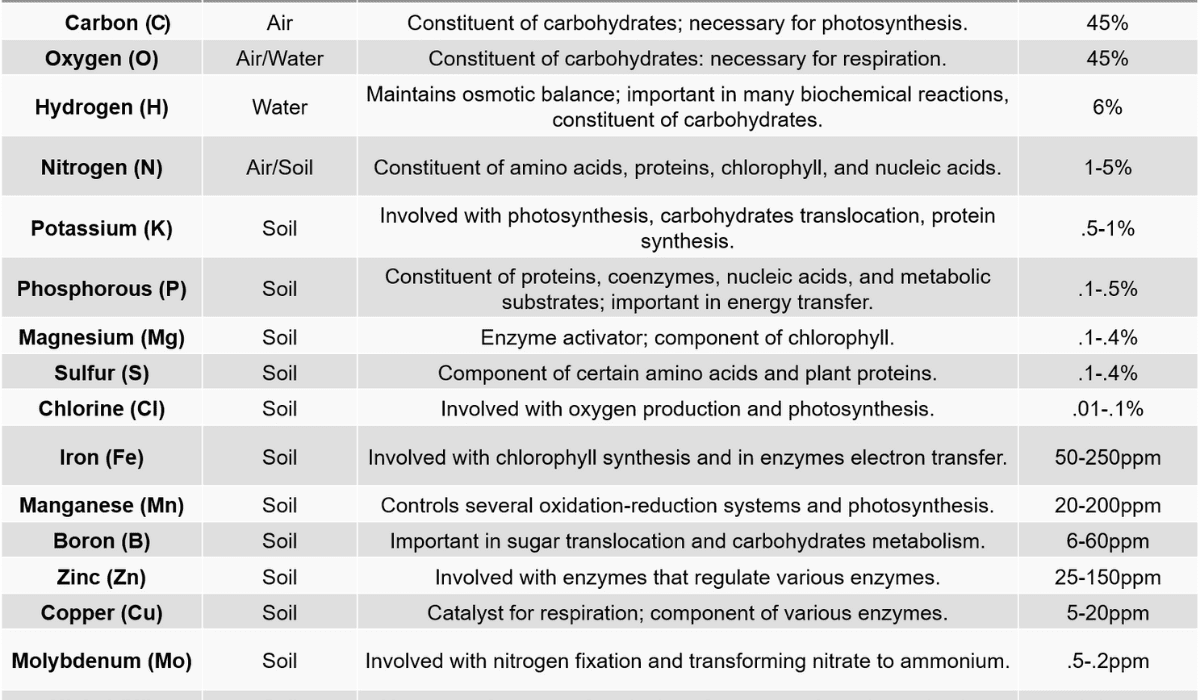
Maize Fodder is a valuable feed source with high energy due to its starch and fiber content. It is also fiber-rich, providing rumen fill and promoting proper digestion. Corn fodder contains essential minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and vitamins, including vitamins A and E. Its nutritional value makes it a beneficial component in animal diets for meeting energy requirements and supporting overall health.
Maize Fodder versus haylage
Corn fodder is a fermented forage made from whole corn plants and is high in energy, making it suitable for livestock with high energy requirements. Conversely, Haylage is fermented grass or legume forage and is typically lower in energy but higher in fiber compared to balancing corn fodder rations.
Maize silage storage methods
Corn fodder can be stored in bunker silos or silage bags, ensuring proper compaction and sealing to prevent air exposure and spoilage. Adequate storage methods help maintain corn fodderi’s quality and nutritional value for animal feeding
Maize Fodder moisture content
The moisture content of balancing maize silage rations typically ranges between 60% and 70%, depending on factors such as the maturity stage at harvest and desired fermentation process. Proper moisture content is crucial for successful fermentation and long-term storage of corn fodder
Maize Fodder fermentation process
During corn fodder fermentation, lactic acid bacteria convert sugars in the corn plant into lactic acid, reducing pH levels and preserving the forage. This process creates a stable and palatable feed with improved digestibility for livestock.
Corn fodder additives
Maize Silage additives such as inoculants or microbial additives can enhance fermentation and improve the stability and nutritional quality of the silage. Other additives like propionic acid can help inhibit spoilage organisms and extend the storage life of balancing corn fodder ration.
Maize Fodder harvesting techniques
maize silage can be harvested using a self-propelled harvester or a tractor-mounted forage harvester. The plants are chopped into small pieces, collected, and packed tightly to minimize air exposure for optimal fermentation.
Conclusion
Balancing maize fodder rations for different livestock species is crucial for optimizing animal health, growth, and production performance. By considering the specific nutritional requirements of dairy cows, beef cattle, swine, and poultry,
farmers can create well-rounded diets that meet the needs of their animals. Regular testing and adjustments ensure that maize silage rations provide the necessary nutrients for livestock to thrive.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQ’s)
How much corn silage should I feed my cows?
The amount of maize silage to feed cows depends on factors such as their weight, production stage, and other feed ingredients in the ration. It is best to consult with a nutritionist to determine the appropriate quantity based on your specific herd’s needs.
Can maize silage be used as the sole feed for pigs?
Corn silage alone may not provide all the necessary nutrients for pigs. It is recommended to balance rations by including other feed ingredients to meet their specific nutrient requirements.
What are the alternatives to corn fodder?
Alternative forage options to maize silage include grass silage, alfalfa silage, and other legume forages. These can be used to diversify rations and provide a mix of nutrients for different livestock
How often should I test the quality of my maize silage?
It is recommended to test balacing corn fodder ration quality at least once a year before feeding to ensure accurate nutrient composition. Additional testing may be necessary if there are significant changes in crop conditions or storage practice
Where can I find more information on balancing livestock rations?
Consult with a qualified nutritionist or veterinarian for personalized advice on balancing livestock rations. Additionally, agricultural extension services, research institutions, and reputable online resources can provide valuable information and guidelines.
Related Articles
Want to purchase top-quality silage? Visit our Agricomplex website to explore our wide range of silage products.
People Also Ask
Are there any risks or concerns when using corn silage in livestock feeding?
Some risks and concerns are associated with using corn silage in livestock feeding. These include the potential for mycotoxin contamination, improper fermentation leading to spoilage or nutrient loss, and the need for proper ration formulation to ensure a balanced diet for the animals.
How is corn fodder used in livestock feeding?
maize silage is commonly used as a primary forage source in livestock feeding, providing energy and fibre for ruminants and monogastric animals. It is incorporated into rations or diets to meet the nutritional needs of livestock, supporting growth, production, and overall animal health.
Why is balancing corn silage rations important?
To meet their specific nutritional requirements, balancing maize silage rations is important to ensure that livestock receives the right proportions of nutrients, such as energy, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Proper balancing optimizes animal performance, growth, reproduction, and overall health.
What are the key nutrients in corn fodder?
The key nutrients in corn fodder include carbohydrates, such as starch and fiber, which provide animal energy. It also contains essential minerals and vitamins, including potassium, magnesium, A, and E.
How do you balance corn fodder rations for dairy cows?
To balance corn silage rations for dairy cows, assess their nutritional requirements and analyze the composition of maize silage. Adjust the inclusion levels of additional feed sources, such as grains, protein supplements, and forages, to meet the cows’ energy, protein, fiber, and mineral needs.