The Bright Future of Corn Silage: Unleashing the Power and Promise
Corn silage is a valuable feed and energy resource in the agricultural sector. It has been a staple for livestock farmers and biogas producers for decades. Its widespread use and versatility have made it necessary for modern farming practices. In recent years, the future of corn silage has been shaped by various innovations and emerging trends that aim to improve corn silage quality.
Table of Contents
Significance of Corn Silage in Agriculture
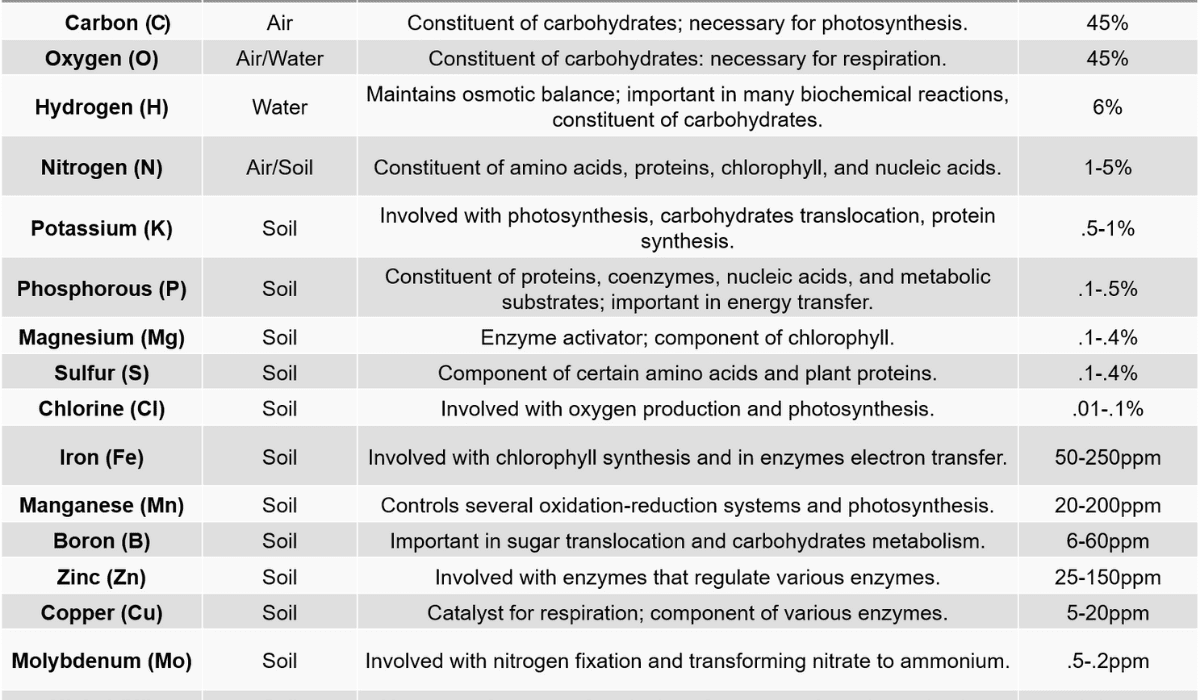
Corn silage plays a vital role in livestock farming. It provides highly nutritious feed for dairy cows, beef cattle, and other ruminant animals. Maize silage is an excellent source of energy, protein, and fiber, contributing to the animals’ growth, health, and productivity. It is also used to make biogas, a renewable energy source that can make electricity and heat.
Traditional Methods of Maize Silage Production
Growing and Harvesting Corn
To make corn silage, farmers first grow corn in special fields. They choose corn varieties that will give them a lot of corn, resist diseases, and work well in their local climate. They take good soil care, use fertilizer, control weeds, and manage pests throughout the growing season. When the corn is fully grown, it’s time to harvest it.
Chopping and Storing
After the corn is harvested, it is chopped into small pieces using special machines called forage harvesters. This helps to break it down and pack it tightly. The chopped corn is then quickly taken to storage structures where it will be stored.
Fermentation
In the storage structures, the corn goes through a fermentation process. Lactic acid bacteria help with this process. It keeps the nutrients in the corn and makes it easier for animals to digest. The storage structures are sealed tightly to keep out air and prevent spoilage and harmful bacteria. Over time, the corn ferments and gets a sour smell.
Innovations in Corn Silage Production
The future of corn silage is being improved through new ideas and technology to make it more efficient, nutritious, and high-quality.
Better Corn with Genetic Modification
Scientists have used genetic modification to create corn varieties with higher yields and better nutrition. These genetically modified organisms (GMOs) have more starch, are easier to digest, and can resist pests and diseases. Thanks to these improved crops, farmers can now grow more corn and produce higher-quality silage.
Smart Farming and Monitoring
New technologies like remote sensing, drones, and soil sensors are changing how corn silage is grown. Farmers can use these tools to watch how their crops grow, find out if they need more nutrients, use water more efficiently, and catch problems early. By using data to make smart choices, farmers can get better crops that yield more and are of higher quality.
Improved Harvesting and Storage
Modern machines for harvesting and storing corn fodder have improved greatly. They can cut the corn at the right length, pack it tighter, and keep air out during storage. These improvements help to keep the nutrients in the corn and prevent it from going rot.
Adding Good Things to Silage
Farmers are also using special products called silage inoculants and additives. These contain helpful bacteria, enzymes, or organic acids that improve fermentation, stop bad bacteria from growing, and make the silage easier for animals to digest. Using these additives makes the fodder more stable and nutritious, which helps the animals grow better.
Trends in Corn Fodder Utilization
Corn silage is a valuable feed for livestock and has other important uses. Here are some notable trends in how it is used:
Feed for Animals
Livestock farmers depend on Maize silage to feed dairy cows, beef cattle, and other animals that chew their cud. It balances energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals well. This helps animals stay healthy, produce more milk, and gain weight. Maize fodder is a cost-effective option compared to feeding them grains, and it can be used in different feeding systems.
Making Renewable Energy
As the need for renewable energy grows, in future of corn silage it has become an important resource for producing biogas. Special plants use a process called anaerobic digestion to turn maize silage into biogas that is rich in methane. This biogas can make electricity, produce heat, or even power vehicles. Using corn fodder for biogas helps us move towards cleaner and more sustainable energy. It reduces the amount of greenhouse gases released.
Corn Silage in Food
Maize silage is finding new uses in the food industry as a useful ingredient and a source of dietary fiber. It can be added to bread, snacks, and breakfast cereals to make them more nutritious and better texture. This aligns with the increasing demand from consumers for natural and sustainable ingredients in their food. These trends show how versatile and important corn fodder is in different industries.
Environmental Impact on Future of Corn Silage
The impact on future of corn silage production and use is significant. To make it more sustainable, we can take certain steps:
Farming Practices that Help the Environment
Farmers can use sustainable practices like conservation tillage, rotating crops, and planting cover crops. These methods reduce soil erosion, improve soil health, and save water. Precision agriculture techniques and careful use of fertilizers and pesticides also lessen the environmental impact.
Recycling and Reusing Byproducts
The leftover parts of corn plants, after making silage, like stalks and cobs, can be recycled for different purposes. They can be used as animal bedding, turned into biofuel, or even used to make bioplastics. By recycling and reusing these byproducts, we reduce waste and use resources better.
Reducing Methane Emissions
When considering the future of corn silage, it becomes crucial to address the environmental impact of its fermentation process. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is released during this phase. However, farmers can adopt proactive measures to mitigate these emissions and ensure a sustainable future for corn silage. By optimizing silage storage techniques and promoting tight packing, farmers can minimize methane release.
Additionally, embracing anaerobic digestion systems allows methane capture and utilization as a renewable energy source. These forward-thinking actions reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to the fight against climate change, securing a greener future for corn silage. These measures can help make maize silage production and use more environmentally friendly.
Common Challenges and Prospects and the Future of Corn Silage
Although the future of corn silage is sustainable due to its great potential, but there are challenges to overcome:
Adapting to Climate Change
Climate change affects maize silage production by changing weather patterns, temperatures, and water availability. Farmers must adjust by using flexible cropping systems. Exploring corn varieties that can handle drought. Thus, improving water management.
Investing in Research and Development
Continuous research and development are crucial for innovation in corn fodder. This involves exploring new hybrid varieties. Improving fermentation processes. Developing new additives and studying the nutritional needs of livestock. Cooperation among researchers, farmers, and industry stakeholders can lead to advancements in corn silage technology.
Market Demand and Consumer Preferences
Understanding market demand and consumer preferences is vital. Consumers are becoming more aware of durable farming practices and prefer natural and healthy food products. Farmers and producers must adjust their practices and products to meet these changing demands.
By addressing these challenges and investing in research, the future of corn silage can be promising as a sufferable and valuable resource.
Conclusion
The future of corn silage looks bright. Ongoing innovations and changing trends are improving how it is made, used, and sustained. Genetic modification, precision agriculture, better chopping and storing techniques, and additives improve maize silage. It is used for feeding animals and making biogas, and there is even interest in using it in food products. Securing the Sustainable Future of Corn Silage; Overcoming Challenges for Market Adaptation and Climate Resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
What is the shelf life of maize silage?
The shelf life of maize silage depends on factors like moisture content, compaction, and storage conditions. Corn silage can last 6 to 12 months or even longer when properly stored.
In Future can silage be used instead of grain?
Yes, In Future of corn silage we can be used as a substitute for grain in animal diets, especially for ruminant animals. It provides them energy, protein, and fiber, making it a valuable feed option.
How does corn fodder contribute to the circular economy?
The future of corn silage is bright. Corn fodder contributes to the circular economy by utilizing agricultural byproducts and converting them into valuable resources for feed and energy. This helps reduce waste and promotes efficient resource use.
Are there concerns about using GMO corn for silage?
Using GMO corn for silage production raises concerns about potential environmental impacts and the safety of genetically modified organisms. Regulations and scientific evaluations are in place to ensure GMO crops’ responsible and safe use.
Can small-scale farmers benefit from producing corn silage?
Yes, small-scale farmers can benefit from producing maize silage. It offers them a cost-effective feed option, improves animal nutrition, and can be integrated into sustainable farming systems. However, proper management practices and suitable equipment are important for successful corn silage production on a smaller scale.
Related Articles
Want to purchase top-quality silage? Visit our Agricomplex website to explore our wide range of silage products.
People Also Asked
How is corn silage made traditionally?
Corn fodder is made traditionally by cutting and fermenting entire corn plants to keep their nutrients.
What is the impact of corn silage on the environment?
Corn fodder impacts the environment, including the possibility of soil erosion, water pollution, and the release of greenhouse gases during production and storage.
How can we make corn silage production more sustainable?
In the Future of corn silage we can make silage production more sustainable by using preservation methods like planting cover crops and managing nutrients precisely.
What are the challenges and future prospects for corn fodder?
Challenges for corn fodder include unpredictable weather patterns, pests, and changes in market demands. The future prospects involve advancements in genetics and the efficient use of resources.
What can we do about the future of corn silage?
To secure the future of corn silage, we should concentrate on sustainable farming methods, genetic progress, better storage techniques, and effective use in animal feed.