Harness the Power of Corn Feedstock: Fueling Success for Livestock
In the world of corn feedstock nutrition, it’s crucial to give animals top-notch feed for their well-being and productivity. corn silage has become a game-changer in farming. This article will delve into its advantages, how it’s made, feeding tips, and more.
Table of Contents
What is Corn Silage?
Corn feedstock refers to the fermented and stored feed made from whole corn plants, including the stalks, leaves, and grain. It is harvested and ensiled at a specific moisture content to preserve its nutritional value. Maize silage serves as a valuable forage option for reflective animals, particularly dairy cows, beef cattle, and sheep.
Benefits of Corn feedstock for Livestock Nutrition
Maize silage is an excellent choice for feeding livestock due to its many nutritional benefits. Let’s explore some of its key advantages:
High Energy Source
Maize silage is known for containing a lot of energy, which makes it an ideal source of fuel for livestock. The grain component of the plant adds to this energy density. Provide animals with the necessary fuel for growth, maintenance, and production.
Good Source of Fiber
Fiber plays a crucial role in animal digestion and rumen function. Corn fodder contains both soluble and insoluble fiber. It is a balanced diet for ruminants. The fiber content helps to maintain rumen health and optimize the digestion process.
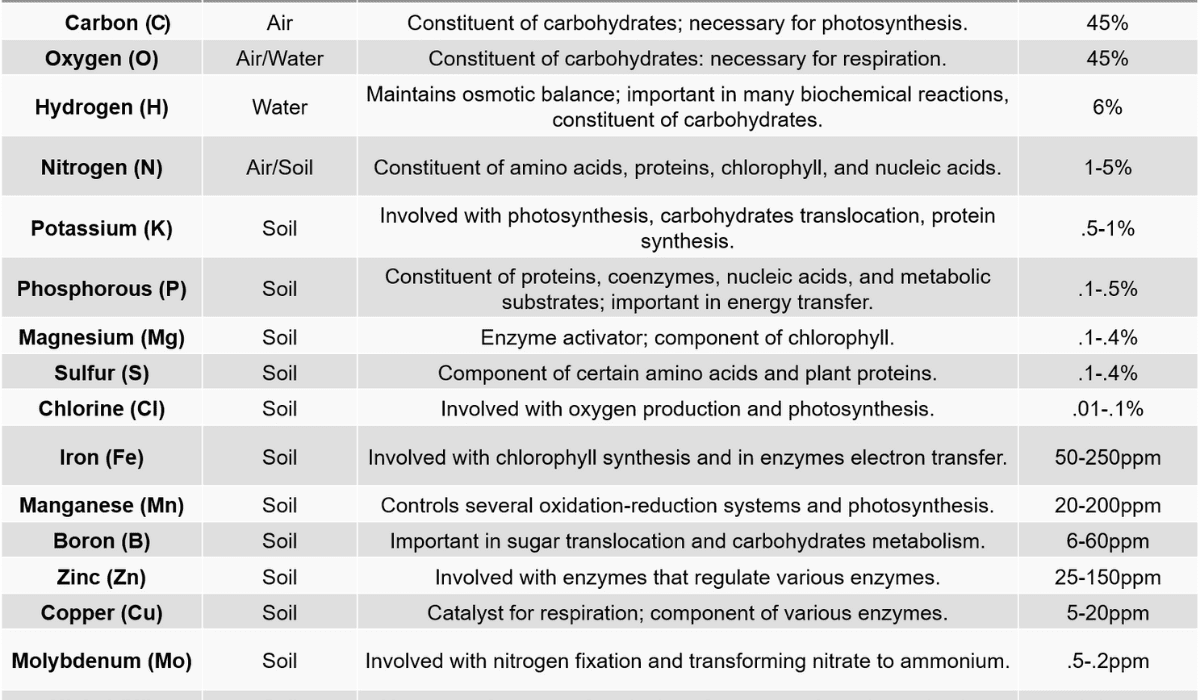
Rich in Minerals and Vitamins
Corn fodder is also great in essential minerals and vitamins. It contains minerals like potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium, which are vital for proper animal growth, bone development, and metabolic processes. Additionally, maize silage is a good source of vitamins A, E, and various B vitamins, supporting overall animal health and immunity.
Increased Milk Production
Dairy farmers rely on maize silage to enhance milk production. It’s a great source of food for cows, giving them lots of energy and making it easier for them to digest. This results in more milk and richer butterfat. Ultimately, it helps dairy cows be more productive.
Health and Performance Benefits
Adding corn fodder to animal feed has many positive effects on health and performance. Corn feedstock balanced nutrients help animals grow, reproduce, and stay healthy. It also keeps the stomach’s acidity stable, preventing digestive problems and imbalances in the body.
Exploring the Livestock Nutrition Value of Corn feedstock
| Nutrient | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| Dry Matter | 30-38 |
| Crude Protein | 7-10 |
| Neutral Detergent Fiber (NDF) | 35-50 |
| Acid Detergent Fiber (ADF) | 20-30 |
| Non-Fiber Carbohydrates (NFC) | 30-40 |
| Ether Extract (EE) | 2-4 |
| Ash | 4-6 |
| Calcium (Ca) | 0.1-0.4 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.2-0.3 |
| Potassium (K) | 1.0-2.0 |
| Sodium (Na) | 0.02-0.10 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 0.10-0.20 |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.10-0.20 |
| Vitamin A (IU/kg) | 15,000-30,000 |
| Vitamin E (IU/kg) | 30-50 |
| Niacin (mg/kg) | 50-100 |
| Thiamine (mg/kg) | 1-2 |
| Riboflavin (mg/kg) | 3-5 |
| Lysine (%) | 0.25-0.35 |
| Methionine (%) | 0.10-0.20 |
| Cystine (%) | 0.10-0.20 |
| Tryptophan (%) | 0.05-0.10 |
The Process of Maize Silage Production
To produce high-quality maize silage, several steps must be followed. Let’s explore the process of making maize silage:
Planting and Harvesting Corn
The process starts with planting corn specifically for silage production. Farmers choose corn hybrids with desirable features for silage, such as high yield and disease resistance. When the corn reaches the ideal growth stage, it is harvested by chopping the whole plant.
Chopping and Fermentation
After harvesting, the corn plants are chopped into small pieces to ensure proper particle size for fermentation. The chopped corn is then tightly packed and covered to create an environment without oxygen. This anaerobic condition allows for fermentation to happen, converting sugars into organic acids and preserving the feed.
Storage and Preservation
Proper storage and preservation techniques are required to maintain the quality of Corn feedstock. Farmers use silos or bunker storage systems to store the silage. The feed is packed to remove air, covered with a plastic layer, and weighted down to prevent spoilage and exposure to oxygen.
Feeding Corn Fodder: How to Do It Right
Feeding corn fodder requires careful attention to certain factors. Here are some guidelines on how to incorporate corn silage into livestock nutrition needs:
Mixing and Rations
To get the most benefits from maize silage, it should be mixed properly with other feed elements. The rations should be balanced to meet the specific nutritional needs of the animals. Dairy nutritionists and livestock advisors can help in creating balanced diets that effectively include corn silage.
Storage and Handling Considerations
Proper storage and handling of Corn feedstock are crucial to maintain its quality. Silos and storage structures should be regularly inspected for any damage or air leakage. It’s also important to prevent spoilage during feeding by using proper feed-out techniques and minimizing exposure to air.
How to improve Corn feedstock Digestibility?
To make Corn feedstock easier to digest, do the following steps:
- Pick the crops when they are fully ripe.
- Make sure to pack the crops tightly to keep air out.
- Keep the moisture level at around 65-70%.
- Use an appropriate inoculant to help with fermentation.
- Take measures to avoid any contamination.
- Include Balance nutrients with extra feeds
- Consider additives like enzymes or organic acids
- Follow good practices for monitoring and feeding the crops
Corn Silage vs. Tradition Feeds
Corn feedstock vs. other livestock Nutrition feeds:
| Livestock Feed | Price (PKR) | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn feedstock | 5000 per ton | Fermented corn plants | High energy content, a good source of fiber | Requires storage facilities, can be expensive |
| Hay | 3000 per ton | Dried grass or legumes | Good source of fiber, low cost | Lower energy content, lower nutrient levels |
| Grain | 8000 per ton | Cereal crops (e.g., corn, wheat) | High energy content, easily digestible | Limited fiber content, can be expensive |
| Soybean Meal | 6500 per ton | Byproduct of soybean oil extraction | High protein content, cost-effective | Limited energy content, requires additional feed components |
| Pasture | Approximately 421800 per acre (depends on land availability) | Fresh grass and vegetation | Natural diet for grazing animals, low cost | Seasonal availability, variable nutrient levels |
What is the Impact of Corn feedstock on livestock performance?
Corn fodder plays a significant role in meeting the nutritional needs of livestock. Here are the key impacts of Corn feedstock:
- Maize fodder is a popular feed for livestock, especially cattle.
- It is made from the entire corn plant, including stalks, leaves, and cobs, which are chopped and stored in a silo.
- Maize silage is a high-energy feed that provides carbs, fiber, and some protein to animals.
- The nutritional composition of Corn feedstock can vary depending on factors like corn plant maturity and fermentation process.
- Livestock can easily digest fodder silage, leading to improved feed efficiency.
- It is a cost-effective feed compared to other forages or concentrates.
- It is rich in energy, supporting weight gain and milk production in dairy cows.
- The fiber in corn fodder promotes rumen function and helps maintain a healthy digestive system in livestock.
- Various livestock species, including cattle, sheep, and goats, can include corn fodder in their diet.
- When properly balanced with other feeds, maize silage can positively impact livestock performance in terms of growth, milk production, and overall health.
Conclusion
Corn feedstock is a game-changer for livestock nutrition. It gives them lots of energy, fiber, minerals, and vitamins. It provides high energy, fiber, minerals, and vitamins. Dairy farmers rely on it for improved milk production and cow health. The production involves planting, harvesting, chopping, fermentation, and proper storage. Maize silage is better than regular feed because it has more energy and nutrients, and it’s cheaper and easier to digest. By understanding the production process, advantages, and feeding guidelines, farmers can optimize livestock nutrition and productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Is Maize silage good for all types of livestock?
Maize silage is often fed to dairy cows and beef cattle. It can also be suitable for other animals like sheep and goats. However, it’s important to think about each animal’s specific needs and preferences.
Can animals eat corn fodder all year?
Yes, animals can eat corn fodder throughout the year. Storing it properly, using airtight structures, and good feeding practices keep the quality of Corn feedstock preserved for a long time.
What’s the right amount of water in Corn feedstock?
The ideal moisture content for corn silage is usually around 65-70%. This level of moisture helps with proper fermentation and nutrient preservation while preventing excessive dryness or spoilage.
How does corn silage compare to other plant options?
Corn silage has several advantages over other plants for feeding animals. It has high energy, is easily digested, and provides a balanced nutrition profile. This makes it a valuable choice for livestock, especially in intensive production systems.
Can small-scale farms grow corn silage?
Yes, small-scale farms can grow corn silage. However, they need to consider factors like available land, equipment, and storage capacity. Successful cultivation and use of corn fodder require farm-specific considerations and good management practices.
Related Articles
Want to purchase top-quality silage? Visit our Agricomplex website to explore our wide range of silage products.
People Also Asked
What are the benefits of maize silage for livestock?
Maize silage provides high energy, fiber, minerals, and vitamins, promotes milk production, and improves animal health and performance.
How is corn silage made?
Corn silage is made by harvesting corn plants at the ideal growth stage, chopping them into small pieces, and tightly packing and covering them to create an anaerobic environment for fermentation.
How should corn fodder be fed to livestock?
Corn fodder should be properly mixed with other feed elements, and balanced rations should be created to meet specific nutritional needs. Proper storage and handling are also important.
How can corn silage digestibility be improved?
To improve digestibility, corn silage should be harvested when fully ripe, packed tightly to exclude air, and maintained at the appropriate moisture level. Inoculants, additives, and good monitoring and feeding practices can also help.
What is the impact of maize fodder on livestock performance?
Maize fodder improves feed efficiency, supports weight gain and milk production, promotes rumen function, and positively affects growth, health, and overall performance in livestock.