Powerful Corn Silage Ration: Maximize Livestock Performance
Corn silage is a vital animal food, and planning corn silage ration is important for their nutrition. This article will discuss balancing energy and fiber in corn silage and planning to keep animals healthy and productive. Farmers and livestock owners can ensure their animals get the best nutrition by understanding the factors that affect energy and fiber, evaluating corn silage quality, and using effective feeding strategies.
Table of Contents
What is Corn Silage?
Corn silage is a valuable feed made from chopped and fermented corn plants. It provides energy, fiber, and nutrients for animals like cows and sheep. It is a good option for a well-rounded and nutritious diet. When corn plants are harvested at the right time, the resulting silage becomes easy to digest and tasty for the animals.
Why is Corn Silage Ration Planning Important?
Proper maize silage ration planning is crucial to meet the specific nutritional needs of different animals. It ensures they get a balanced diet with the right nutrients for growth, reproduction, and maintenance. Ration planning also helps animals use their feed efficiently, reduces costs, and lowers the risk of health problems. Finding the right balance of energy and fiber for corn silage is key to keeping animals healthy and performing well.
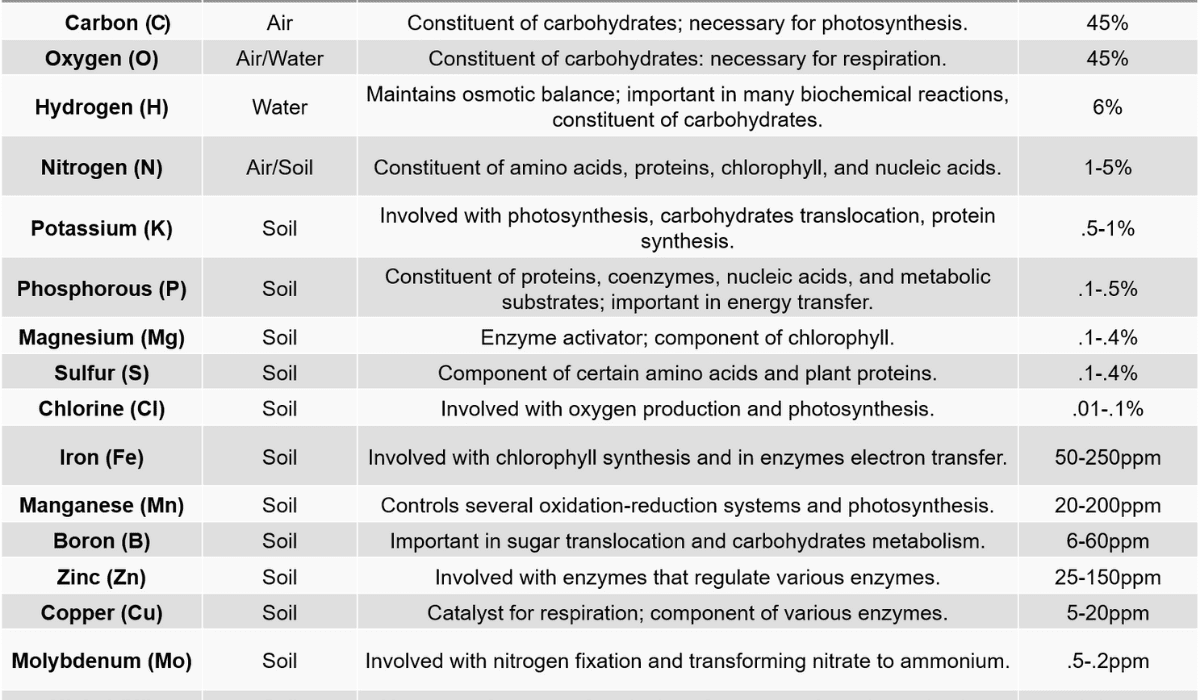
Understanding Energy and Fiber in Corn Silage
Energy and fiber are important factors in ensiled corn forage that affect how animals are nourished. Energy, measured by total digestible nutrients (TDN) or net energy (NE), provides the energy animals need for growth, milk production, and overall metabolic processes. Fiber, conversely, is a complex carbohydrate that helps with digestion in the rumen, keeps digestion healthy, and prevents digestive problems.
Factors Affecting Energy and Fiber Levels
Several factors influence how much energy and fiber are in corn silage. These include the type of corn used, the stage of the plant’s growth when it was harvested, the conditions in which it grew, and how it was harvested. Choosing the right type of corn with characteristics like high starch content and digestibility can make a big difference in energy and fiber levels.
Finding the Right Energy and Fiber Levels
To determine the best energy and fiber levels in corn silage diet, it’s important to consider the specific needs of the animals you’re feeding. Different animals have different nutritional requirements based on their age, weight, stage of production, and health conditions. Regularly analyzing the forage is crucial to know the nutrient composition of the corn silage, including its energy and fiber content.
Evaluating Corn Silage Quality
The quality of corn silage diet directly affects its nutritional value and how well animals perform. Several factors should be considered to assess its quality, such as moisture content, dry matter content, fermentation characteristics, and the presence of molds or harmful substances called mycotoxins. You can evaluate quality through visual inspection, laboratory analysis, and tools like the kernel processor score and fermentation profile.
Balancing Energy and Fiber in Ration Planning
To balance energy and fiber in corn silage ration planning, it’s important to understand the energy needs of the animals and the fiber content of the forage. The energy requirements of the maize silage ration depend on factors like maintenance, growth, reproduction, and milk production. The fiber requirements are influenced by the animal’s stage of development and the desired fermentation pattern in the rumen.
Calculating Energy and Fiber Requirements
Accurately calculating energy and fiber requirements involves considering the animal’s weight, daily energy needs, and the desired energy and fiber intake from corn silage. Established equations or online tools provided by universities or agricultural institutions can help with these calculations. By determining the specific energy and fibre targets, farmers can create well-balanced rations for their animals.
Considerations for Different Livestock Species
Different livestock species have different dietary needs, and their ability to use energy and fiber from corn silage varies. For example, dairy cows need corn silage rations with high energy content to support milk production, while beef cattle may benefit from higher fiber levels in their maize silage ration for rumen health. Sheep and goats also have specific requirements that should be considered when planning their fermented corn feed.
Feed Additives and Supplements
In some cases, feed additives and supplements may be necessary to optimise the energy and fibre balance in corn silage rations. These additives can include products that modify the rumen, enzymes, buffers, or specific fibre sources. However, it’s important to consult with a nutritionist or veterinarian before adding any additives or supplements to the diet.
Ensuring Proper Storage and Preservation of Corn Silage
Proper storage and preservation techniques are critical to maintaining the quality of corn silage. This includes using adequate storage structures, such as silos or bunkers, to minimize exposure to oxygen and prevent spoilage. Employing appropriate fermentation practices, such as using a silage inoculant, can also enhance preservation and minimize nutrient losses.
Understanding Feed Conversion Ratio in Corn Silage Rations
Definition: Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) measures the efficiency of converting feed into desired outputs, such as weight gain or milk production, in corn silage.
Calculation: FCR is determined by dividing the amount of feed consumed by the desired output achieved, such as pounds of weight gained or liters of milk produced.
Importance: FCR helps assess corn silage rations’ economic and nutritional efficiency, enabling better decision-making in feed management.
Lower is Better: A lower FCR indicates higher efficiency, as less feed is required to achieve the desired output in rations.
Factors Affecting FCR: Feed quality, nutrient content, animal genetics, health, and management practices influence FCR in Maize silage rations.
Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitoring FCR and adjusting feed composition and management practices can help optimize efficiency and reduce costs in maize silage ration
Enhancing Nutrient Availability in Corn Silage Ration Planning
Feed Analysis: Conduct regular feed analysis to determine the nutrient content of maize silage ration components.
Balancing Nutrients: Use the feed analysis results to balance the ratio, ensuring optimal nutrient levels for the desired animal performance.
Consider Supplemental Feeds: Incorporate supplemental feeds or additives, such as protein sources or mineral supplements, to address any nutrient deficiencies in the corn silage ration.
Feed Processing: Utilize appropriate feed processing techniques, such as grinding or pelleting, to enhance nutrient availability and digestion in the maize silage ration.
Optimal Feed Mixing: Ensure thorough and consistent mixing of all ration components to achieve uniform nutrient distribution and availability in the corn silage ration.
Consult with a Nutritionist: Seek guidance from a professional animal nutritionist to develop a well-balanced maize silage ration that maximizes nutrient availability and supports animal health.
Feeding Strategies and Management Practices
Implementing effective feeding strategies and management practices is crucial for optimizing corn silage utilization. These strategies may involve proper feed out management to minimize spoilage and maintain consistency in the ration. Adjusting feed delivery based on animal needs, monitoring feed intake, and ensuring access to clean water and adequate shelter are also important aspects of effective feeding management.
Monitoring and Adjusting Rations
Regular monitoring of animal performance and feed efficiency is necessary to assess the effectiveness of corn silage ration planning. By closely observing feed intake, body condition, milk production, and growth rates, farmers can identify any imbalances or deficiencies in the ration. Based on these observations, adjustments can be made to optimise the energy and fiber balance and ensure the best possible outcomes.
Benefits of Effective Corn Silage Ration Planning.
Effective fermented corn feed planning benefits farmers and livestock in several ways:
- Enhances animal performance, milk production, and supports healthy growth.
- Effective corn silage ration planning improves overall herd or flock health by providing the right combination of energy and fiber for optimal rumen function, nutrient absorption, and digestion in livestock.
- Reduces feed costs and increases feed efficiency, leading to cost savings for farmers.
- Minimises the risk of metabolic disorders by ensuring a balanced diet and preventing nutritional imbalances.
- Maize silage ration Improves reproductive performance, resulting in better fertility rates and successful breeding programs.
- Optimises feed resources by managing energy and fibre levels, reducing waste, and maximising the utilisation of corn silage.
Achieving Nutritional Balance in Corn Silage Rations.
Components in the maize silage ration.
Nutrient Requirements: Determine specific nutritional needs based on age, weight, and production goals.
Ration Balancing: Adjust feed amounts to meet nutrient requirements in the corn silage ration.
Protein and Energy: Provide adequate protein and energy for growth, maintenance, and performance.
Vitamins and Minerals: Include essential vitamins and minerals in the maize silage ration for overall health.
Monitor and Adjust: Regularly assess animal performance and adjust the corn silage ratio.
Conclusion
Corn silage ration planning is a crucial aspect of livestock management. Farmers can ensure optimal animal nutrition by balancing energy and fiber in fermented corn feeds, leading to improved performance, health, and overall farm profitability. Effective ration planning not only benefits the animals but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices. By considering the specific needs of different livestock species and implementing appropriate feeding strategies, farmers can achieve the best possible outcomes for their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Can corn silage be fed to non-ruminant animals?
A: Corn silage is primarily used as a feed in corn silage rations for ruminant animals, as their digestive system is better suited to process the fiber and nutrients in silage.
How often should I evaluate the quality of my corn silage?
A: It is recommended to evaluate the quality of corn silage at least once a year, preferably before the feeding season begins. Regular monitoring can help identify changes or issues affecting animal nutrition.
Can corn silage be included in the diet of horses?
A: While horses can consume small amounts of corn silage, it should be used cautiously due to their sensitive digestive system. Horses have specific dietary requirements, and their diets are typically based on forages such as hay or pasture.
Can corn silage rations be adjusted for animals during different production stages?
A: Yes, different production stages have varying nutritional requirements. Adjustments should be made to maize silage rations to meet the specific needs of growing animals, lactating cows, or animals in different stages of reproduction.
Can poor-quality corn silage ration be salvaged for feeding?
A: Poor-quality fermented corn feed can be improved by blending it with higher-quality forages or adding supplements to enhance its nutritional value. However, consulting with a nutritionist or veterinarian before feeding poor-quality hay is essential to avoid adverse effects on animal health.
Related Articles
Want to purchase top-quality silage? Visit our Agricomplex website to explore our wide range of silage products.
People Also Asked
How does corn silage ration planning benefit livestock?
Maize silage ration planning benefits livestock by providing a balanced and nutritious diet that enhances animal health, performance, and overall well-being.
What factors should be considered when balancing energy and fiber in corn silage ration planning?
When balancing energy and fiber in corn silage ration planning, factors such as livestock species, stage of development, energy requirements for growth and production, and desired rumen fermentation pattern should be considered to ensure optimal nutrition and digestion in animals.
How does corn silage ration planning reduce feed costs?
Ensiled corn forage planning reduces feed costs by optimizing feed efficiency, minimizing waste, and maximizing the utilization of corn silage as a cost-effective source of energy and nutrients for livestock.
What are the potential risks of metabolic disorders in livestock, and how does corn silage ration planning minimize them?
Effective fermented corn feed planning improves reproductive performance in livestock by providing the necessary energy and nutrients for better fertility rates and successful breeding programs.