Unleash The Powerful Impact of Corn Silage
Milk is important in the dairy industry. Farmers want to get lots of good milk from their cows. One important thing that affects milk production is what the cows eat. It’s crucial to give cows a diet that has the right amount of energy, protein, and fiber. One food that is really popular for cows is corn fodder. In this article, we will talk about what’s in corn fodder and how the impact of corn silage on milk production, the best ways to use it, and how it helps cows stay healthy.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Dairy farmers know that giving their cows a good and healthy diet is really important for making lots of milk. Corn silage is a type of food made from whole corn plants, and it’s become a really good choice for feeding dairy cows. It’s popular because it has a lot of good nutrients, and it helps cows make more milk.
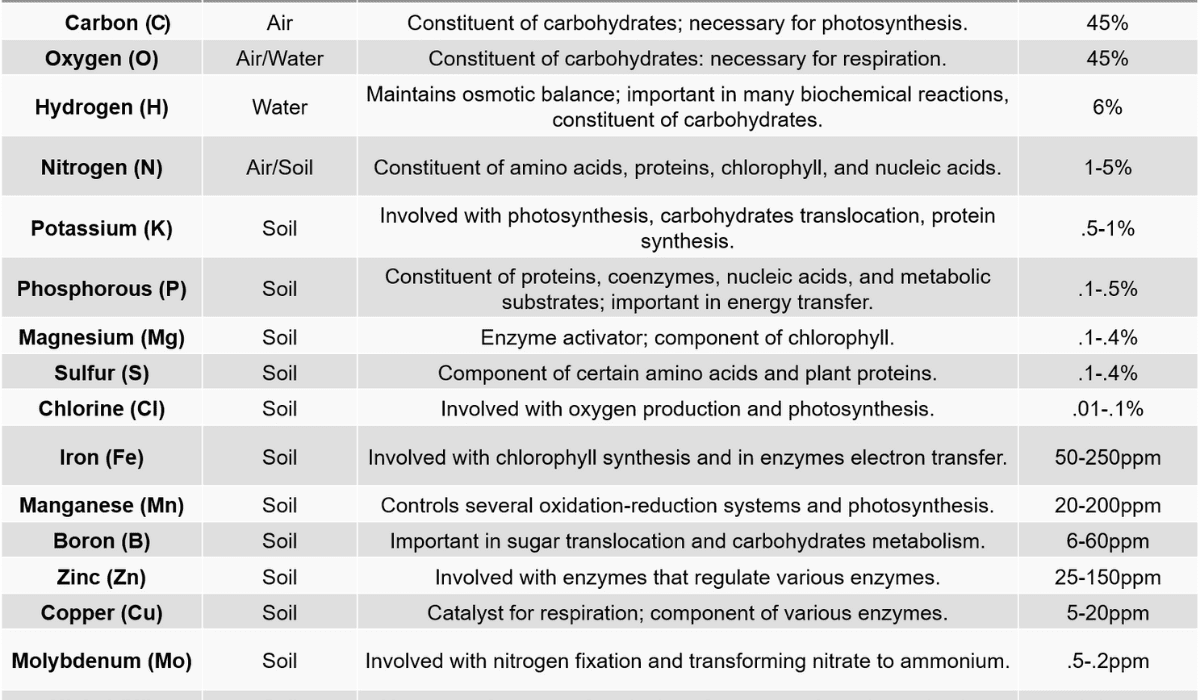
Nutritional Composition Impact of Corn Silage
Corn silage has a lot of important nutrients that help dairy cows stay healthy and produce a lot of milk. It’s made from the whole corn plant, including the stalks, leaves, cobs, and grain. The corn plant is harvested when it’s at a certain stage of growth. The nutrients in corn forage can vary depending on things like the type of corn, how it was grown, and how it was stored.
Maize ensilage has a lot of carbohydrates, which give energy to dairy cows. The carbohydrates in corn fodder come from starch, fiber, and sugars. It also has proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals that are really important for the cow’s body and for making milk.
Benefits of Corn Silage in Milk Production
The inclusion of maize silage in the diet of dairy cows offers numerous benefits that positively impact of corn silage on milk production. Here are some key advantages:
- Lots of Energy: Corn silage has a ton of energy that cows can easily digest, so they can make a lot of milk.
- Nutritionally Balanced: Corn silage has a mix of nutrients that give cows a well-rounded diet, helping them stay healthy and productive.
- Easy to Digest: silage gets easier to digest through the fermentation process when it’s stored, so cows can absorb its nutrients better.
- Healthy Stomach: The fibre in maize silage helps cows’ stomachs work well, which means their bodies can use the nutrients better.
- Steady Milk Production: If cows eat corn silage regularly, their milk production stays steady all year round. It doesn’t go up and down like it can with other foods.
Feeding Corn Silage to Dairy Cows
To maximize the benefits of corn silage, it is essential to incorporate it effectively into the diet of dairy cows. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- Balanced Rations: Dairy farmers should work with nutritionists to develop balanced rations that include an appropriate proportion of corn fodder based on the cow’s nutritional requirements.
- Gradual Transition: When introducing corn forage into a cow’s diet, it is crucial to do so gradually, allowing their digestive system to adjust to the new feed source.
- Proper Mixing: Corn silage should be mixed thoroughly with other ingredients to ensure uniform nutrient distribution and encourage consistent intake by the cows.
- Regular Monitoring: Dairy farmers should monitor cow performance, milk production, and body condition score to assess the effectiveness of corn fodder inclusion in the diet.
Different Varieties of Impact of Corn Silage on milk production
| Varieties of Corn Silage | Impact on Milk Production |
|---|---|
| High-Quality | This type is great for milk production because it’s easy for cows to digest and has lots of nutrients. |
| Low-Quality | This type doesn’t have as many nutrients, so it can lead to less milk production. |
| BMR (Brown Midrib) | This type is really good for milk production because it’s easy to digest and has a lot of energy. It also helps cows’ stomachs stay healthy. |
| Leafy | This corn forage has the potential to increase milk production because it has a lot of nutrients and is easy to digest. It’s made up of more leaves and fewer stalks, which makes it better for cows. |
| Starch-Rich | This type can increase milk production because it has a lot of starch, which gives cows energy. |
| High-Moisture | The impact of corn silage on milk production can vary with this type. Farmers might need to adjust how they feed cows and the food mixture. |
| Whole-Plant | This type silage has a moderate impact on milk production. It includes the whole corn plant, like the leaves, stalks, and ears. |
| Bicolor | This type of silage has a similar impact of corn silage on milk production as regular yellow. The nutrients and how easy it is to digest. |
| Organic | This type of silage has a moderate impact on milk production. It includes the whole corn plant, like the leaves, stalks, and ears. |


Impact of Corn Silage on Management and Storage
Proper management and storage of corn silage are vital to maintaining its nutritional quality. Here are some best practices:
- Harvesting: Corn plants should be harvested at the optimal stage of maturity to ensure maximum nutrient content in the silage.
- Chopping and Processing: Corn plants should be chopped into small pieces to encourage proper fermentation and minimize spoilage.
- Ensiling: Ensuring proper compaction and removal of oxygen during the ensiling process is crucial for reducing spoilage and preserving nutritional quality.
- Storage: Corn silage should be stored in airtight silos or bunkers to protect it from air exposure and maintain its nutritional value.
Maximizing Milk Production with the Impact of Corn Silage
In addition to incorporating on the impact of corn silage into the diet, several strategies can further optimize milk production in dairy cows. These include:
- Adding special things to corn silage can help cows’ stomachs work better, help their bodies use the nutrients, and make more milk.
- Using fancy technology like automated feeding systems can give each cow exactly the right amount of food so they get all the nutrients they need.
- Dairy farmers should work with nutritionists to make a schedule for feeding cows that gives them the best milk production. The timing and how often they eat can make a big difference.
- Breeding programs that focus on picking cows with a lot of milk potential can help make the most of maize ensilage and get the most milk.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While corn silage offers numerous benefits, there are some potential challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Mycotoxin Dangers: Sometimes, corn silage can have harmful substances called mycotoxins, which can make cows sick and lower milk production. Regular testing and storing the silage properly can help prevent this problem.
- Nutrient Differences: The nutrients in maize ensilage can be different depending on things like how it was grown and stored. Farmers should test the silage regularly to know what nutrients are in it and adjust the cows’ food accordingly.
- Introducing New Foods: If farmers want to give cows new types of food or change their diet a lot, they need to be careful. Cows’ stomachs can get upset, so it’s important to watch them closely and make changes gradually.
Case Studies and Success Stories on the Impact of Corn Silage
Real-life examples demonstrate the positive impact of corn silage on milk production. Many dairy farms have reported significant improvements in milk yield, cow health, and overall farm profitability after incorporating corn silage into their feeding programs. These success stories serve as inspiration for other farmers looking to optimize their milk production.


Future Trends and Innovations
The field of corn silage production continues to evolve, with ongoing research and technological advancements driving future trends. Some emerging areas of focus include:
| Harvesting with Precision: New technologies and equipment help farmers know the best time to harvest corn for silage. This makes sure the corn has the most nutrients possible. |
| Boosting Nutrition: Scientists are looking into ways to make corn silage even more nutritious. They are studying methods like biofortification to add more nutrients to the corn or using special types of corn that already have better nutrients. |
| Better Storage: Researchers are working on ways to store corn fodder so it doesn’t spoil and keeps its nutrients for a long time. This helps farmers have good-quality silage even when they store it for a while. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, The Impact of corn silage is very important for a lot of milk production and keeping dairy cows healthy. It has a lot of good nutrients and gives cows the energy they need. By adding corn silo to the cows’ food, following the right feeding methods, and dealing with issues like mycotoxins and nutrient differences, farmers can get the most out of it. The impact of corn silage on dairy farms is profound, utilizing ongoing research and new technology to ensure sustainable milk production and overall success.
Frequently Asked Question
Can corn silage be fed to other livestock besides dairy cows?
Yes, corn fodder can be a valuable feed source for beef cattle, sheep, and other ruminant animals.
How does impact of corn silage compare to impact of other forages in terms of milk production?
Corn forage is known to provide higher energy content and better digestibility compared to many other forages, making it highly beneficial for milk production.
Are there any risks associated with feeding corn silage to cows?
While corn silage is generally safe and beneficial, mycotoxin contamination and nutrient variability can pose challenges. Regular testing and proper storage practices help mitigate these risks.
Can corn silage be included in the diet of dry cows or heifers?
Yes, corn forage can be incorporated into the diets of dry cows and heifers, tailored to their specific nutritional requirements.
Where can I find more information on optimizing corn silage usage?
Dairy extension programs, agricultural universities, and reputable dairy industry publications are excellent sources for in-depth information on corn fodder usage and management.
Related Articles
Looking to enhance your knowledge about silage? Explore our informative blog posts on the topic.
Want to purchase top-quality silage? Visit our Agricomplex website to explore our wide range of silage products.
People Also Asked
How is corn silage used in milk production?
Corn silage is used as a feed for dairy cows to support milk production. It is made by fermenting chopped corn plants.
Does corn silage affect milk quality?
Properly managed corn silage does not negatively impact milk quality, but factors like harvest maturity and storage conditions can influence milk composition.
What are the of using corn silage in dairy farming?
Corn silage provides energy and nutrients, supports milk production, is cost-effective, and helps utilize surplus corn crops.
Are there any disadvantages to using corn silage in milk production?
Improper fermentation or storage can lead to spoilage, mould growth, and potential negative effects on cow health and milk quality.
How much corn silage should be fed to dairy cows?
The amount of corn silage fed depends on factors like cow weight, lactation stage, and dietary needs, typically ranging from 30% to 60% of dry matter intake.
Can corn silage replace other types of feed in milk production?
While corn silage is a valuable feed, it generally cannot replace all other types of feed due to potential nutrient imbalances. A balanced diet is crucial for optimal milk production.