Building Blocks of Water Conservation: Discover the Essential Parts
Water conservation is an innovative and effective way to give plants the necessary water. Unlike traditional methods that spray water everywhere, water conservation slowly delivers water to the plant’s roots. This article explores some advanced techniques for water conservation that make it work even better.
Introduction
Water conservation from drip irrigation, which brings water directly to the plant’s roots, utilizes small tubes or pipes with unique parts that release water slowly and evenly. This method is popular due to its advantages over other watering techniques, promoting the efficient use of water resources and supporting sustainable agriculture.
Table of Contents
Benefits of drip irrigation
The benefits of water conservation are that it saves water, keeps plants healthy, helps crops grow better, and prevents weeds. Delivering water gives plants just the right amount of moisture without wasting any. Water conservation practices can also be adjusted to fit the needs of different plants, making it a great way to rinse them.
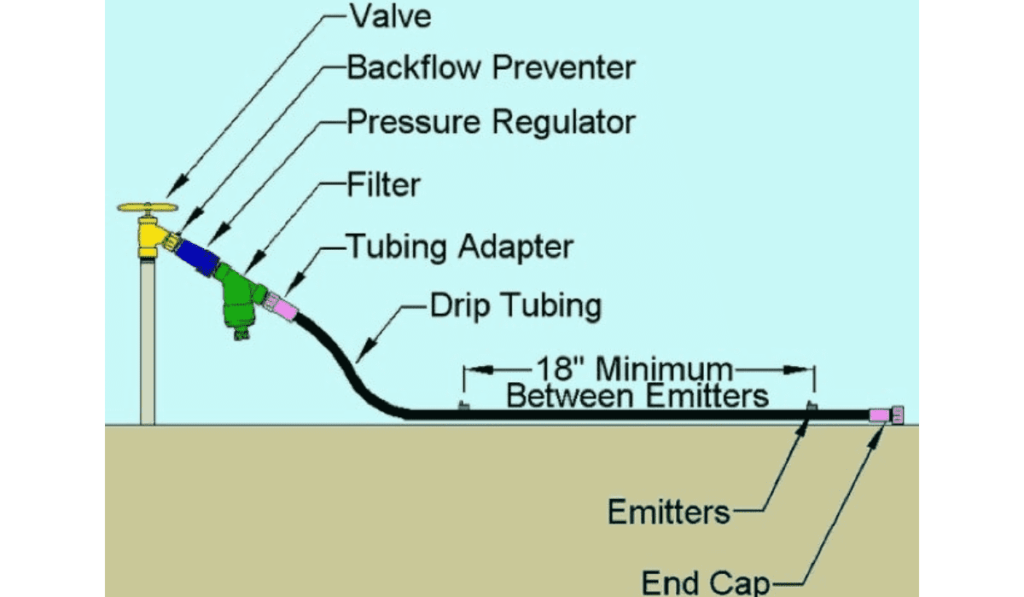
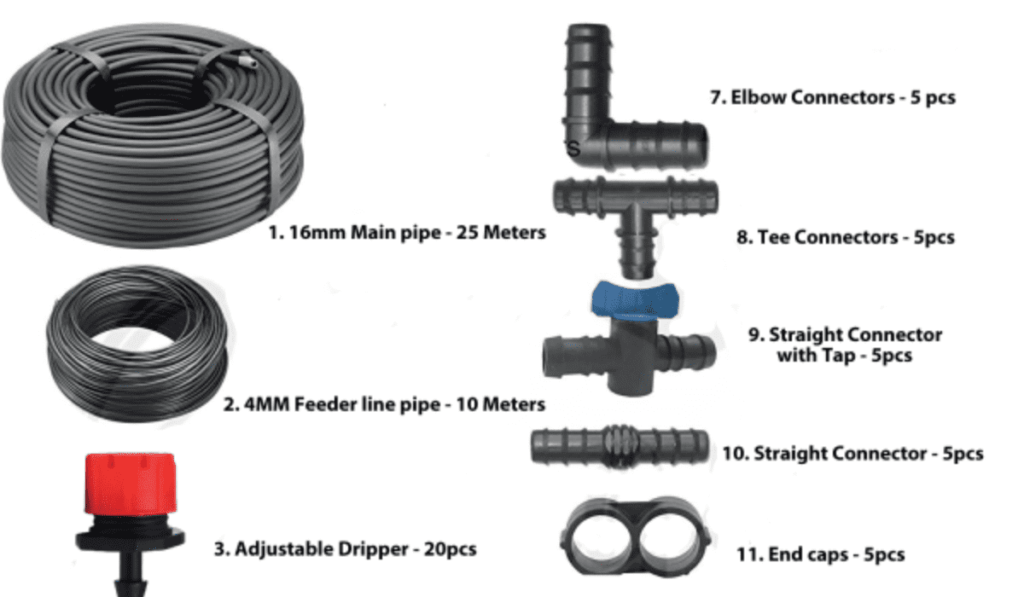
Parts of the Drip Irrigation System
To understand the advanced techniques in water conservation, we need to know about the essential parts of the system. These parts work together to ensure the water is distributed and the system works properly.
Drip emitters:
Drip emitters are special devices that release water in a controlled way. They come in different types, like pressure-compensating emitters, adjustable emitters, and dripper lines. Pressure-compensating emitters ensure the water flow stays the same even if the pressure changes, so it gets spread evenly.
Pressure regulator:
A pressure regulator is an important part that keeps the water pressure steady in the drip irrigation system. It stops the pressure from getting too high, which could clog or damage the emitters. This helps the system work at its best.
Filters:
Filters stop dirt, sand, and other things from getting into the drip irrigation system. They keep the emitters clean and clear so the water can flow without any problems. This keeps the system running smoothly and lasting longer.
Backflow preventer:
A backflow preventer is installed to prevent contaminated water from returning to the main water supply. It ensures the water used for irrigation doesn’t mix with clean drinking water. This keeps the irrigation system safe and protects the environment.
Designing a Drip Irrigation System
To create an effective drip irrigation system for water conservation, you need to think about a few essential things. Here are the key points to consider:
| Figuring out how much water you need: Knowing how much water your plants require is essential to design a sound drip irrigation system. You have to consider things like the type of plants you have, their growth stage, the climate you’re in, and the soil condition. These factors will help you determine how much water you need and how often to water your plants. |
| Deciding where to put the water outlets: The placement of the water outlets, called emitters, is crucial for ensuring the water is distributed evenly across the planting area. This depends on the water needs of your plants, the type of soil you have, and the slope of the land. Proper placement of the emitters prevents your plants from being underwatered or overwatered and helps them thrive. |
| Choosing the suitable size pipes: Selecting the correct pipe size is essential to maintain the proper water pressure and flow rate. The size of the pipes depends on things like the pressure of your water source, how long your system is, and the rate at which water needs to flow. |
Installation Process
Proper installation is crucial for your drip irrigation system to work well. Here are the steps you need to follow:
- Getting the area ready: Before you start installing the system, make sure to remove any rocks, debris, or weeds from the area. This will simplify the installation process and reduce the chances of damaging the system.
- Installing the emitters and fittings: Attach the drip emitters, fittings, and connectors to the sub-mainlines. Place the emitters close to the plants so they cover the roots adequately. Make sure to tighten the fittings and connectors securely to prevent any leaks.
- Placing the mainline and sub-mainlines: Begin by laying out the mainline, which connects the water source to the planting area. Then, connect the sub-mainlines to the mainline. The sub-mainlines deliver water to specific zones or rows.
Best practices for advanced drip irrigation
When using advanced drip irrigation techniques, following these practices can help you use water more efficiently, improve how well it works, and get the most out of your crops:
Soil and Water Management:
- Test the soil to see how much water it can hold and how quickly it absorbs water.
- Use sensors or tensiometers to check the moisture in the soil and avoid giving it too much or too little water.
- Use mulching to cover the soil and keep the water from evaporating too quickly.
- Try things like contour ploughing, terracing, or cover cropping to help save water in the soil.
System Design and Layout:
- Use drippers or emitters that distribute water evenly, especially in long irrigation lines or areas with different elevations.
- Use devices like pressure regulators and gauges to control the water flow and ensure the system isn’t damaged.
- Decide where to put the drip lines or emitters based on what the crops need, the soil type, and the water available.
- Divide the irrigation system into zones based on the crops’ water needs. This way, you can control the water better.
Automation and Monitoring:
- Use technology like soil moisture sensors and weather-based controllers to decide when to water and how much to use automatically.
- Install monitoring systems that let you check how well everything works and get alerts if something goes wrong.
- Connect the irrigation system to a central farm management system or software so you can analyze data and make better decisions.
System Maintenance and Management:
- Regularly check and clean the filters to prevent clogging and ensure the water flows nicely.
- Fix leaks, damaged lines, or broken emitters quickly to avoid wasting water.
- Plan regular maintenance to replace worn-out parts, check the valves, and make sure the system works properly.
- Train the farm staff on how to use and take care of the system so they can avoid mistakes and keep everything running smoothly.
Fertigation and Nutrient Management:
- Use fertigation by adding fertilizers or nutrients to the irrigation system. Make sure to use the right amount so you don’t overdo it.
- Test the soil and plant tissue regularly to see what nutrients are needed and adjust the fertilizer accordingly.
- Use organic fertilizers or soil additives to keep the drip system and deliver nutrients effectively.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation:
- Keep up with the latest water conservation techniques and try new methods that suit your farm’s needs.
- Attend workshops, seminars, and conferences to learn from experts and share your experiences with other farmers.
- Keep records of your irrigation schedule, how well the system works, and how the crops respond. This will help you make better decisions based on data.


Advanced Techniques of Water Conservation
As drip irrigation technology advances, some advanced techniques can enhance its effectiveness. Here are a few special techniques.
Pressure-compensating emitters:
These emitters provide a consistent flow rate regardless of changes in water pressure. This ensures that water is distributed evenly, even in areas with varying elevations or long irrigation lines.
Fertigation:
Fertigation is the process of applying fertilizers through the water conservation. It allows for precise and controlled delivery of nutrients directly to the plant roots, improving nutrient uptake and plant health.
Automation and control systems:
Automation and control systems enable remote monitoring and control of the drip irrigation system. These systems can be programmed to adjust watering schedules, monitor soil moisture levels, and optimize water usage based on weather conditions.
Environmental Considerations
Drip irrigation offers several environmental benefits compared to traditional methods. Here are some essential things to consider.
Water conservation:
Drip irrigation significantly reduces water usage by delivering water directly to the plant roots. It minimizes evaporation and runoff, making water use more efficient.
Use of recycled water:
Drip irrigation systems for water conservation can be designed to use recycled or reclaimed water sources, reducing the need for freshwater. This promotes sustainable water management practices.
Impact on soil health:
Drip irrigation promotes better soil health by minimizing soil erosion and compaction. It allows for controlled watering, preventing oversaturation and nutrient loss.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Many farmers and agricultural businesses have seen significant benefits from using drip irrigation. Here are a few examples:
Improved crop yields:
Farmers using drip irrigation have reported increased crop yields due to better water efficiency and healthier plants. Fruits, vegetables, and cash crops have shown remarkable improvements in both quality and quantity.
Water savings:
Drip irrigation has been proven to save significant water compared to traditional methods. Studies have shown up to 50% water savings in various agricultural and horticultural applications.
Conclusion
Advanced techniques in water conservation have revolutionized plant watering, offering improved efficiency, water conservation, and better plant health. Farmers and gardeners can optimize their irrigation practices by using pressure-compensating emitters, practicing fertigation, and adopting automation. Water conservation’s environmental advantages, such as water conservation and soil health improvement, make it a sustainable choice for the future.
Get your 8/12 PVC Branch Pipe Micro Spray for Drip Irrigation, Garden Irrigation, and more at Agricomplex. Don’t wait, shop now!

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
How much water can be saved with drip irrigation?
Water conservation from Drip irrigation can save up to 50% of water compared to traditional irrigation methods, as it delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff.
Can drip irrigation be used for all types of crops?
Drip irrigation suits various crops, including fruits, vegetables, flowers, and trees. It can be customized to meet the specific water requirements of different plants.
How long does a drip irrigation system last?
A well-maintained drip irrigation system can last for 15 to 25 years. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning filters and replacing damaged components, ensures longevity.
Is drip irrigation cost-effective?
While the initial setup cost of a drip irrigation system may be higher than traditional methods, the long-term benefits, including water savings and improved crop yield, make it cost-effective in the long run.
Can drip irrigation be used in hilly terrain?
Drip irrigation can be used in hilly terrain with proper design and planning. The system can be customized to accommodate elevation changes and deliver water effectively to all areas.
Related Articles
Looking to enhance your knowledge about Drip irrigation? Explore our informative blog posts on the topic.
looking to purchase a Drip irrigation accessories for Water conservation? Visit our Agricomplex website. Easy and helpful information just for you!
People Also Asked
What are the benefits of advanced drip irrigation techniques?
The benefits of advanced drip irrigation techniques include improved water efficiency, increased crop yields, reduced weed growth, and enhanced nutrient delivery.
How does drip irrigation conserve water?
Drip irrigation conserves water by delivering water directly to the plant’s root zone, minimizing evaporation and reducing water waste.
What types of crops can benefit from advanced drip irrigation?
Advanced drip irrigation can benefit various crops, including vegetables, fruits, row crops, orchards, vineyards, and even landscape plants.
Are there any specific tools required for advanced drip irrigation?
Specific tools required for advanced drip irrigation include drip emitters, pressure regulators, filters, drip lines, valves, and controllers.
How do I determine the proper spacing for drip irrigation systems?
To determine the proper spacing for drip irrigation systems, consider plant water needs, soil type, climate, and desired water distribution uniformity.




